Have you tried using AI to solve a problem, only to end up with unpredictable or inaccurate results? One key reason is that we often rely on generative AI (G-AI), which produces outputs that can vary significantly over time. Today’s result might differ tomorrow, even with the same input. This is the nature of G-AI — it’s dynamic, evolving, and influenced by continuous training, feedback, and platform updates.
G-AI also has limited memory, often forgets past responses or relies too heavily on them, leading to confusion or repeated questions. Tasks may fail due to errors, incomplete logic, or poor decision-making, resulting in various failures.
Why Generative AI Alone Falls Short
There are many reasons why AI as a standalone problem solver shouldn’t be considered at this time. Here are some of the most important ones:
- High Error Margin: Even OpenAI’s ChatGPT warns users: “ChatGPT can make mistakes. Check important info.” This is a clear admission that AI, at least for now, has noticeable errors.
- Unpredictability: G-AI behavior can shift unexpectedly as it evolves. This makes it difficult to ensure consistent outcomes - a critical issue in business applications that could result in losses.
- Natural Language Dependency: G-AI relies on human language (via LLMs), which is ambiguous. In contrast, mathematical or logical languages (like Propositional Logic) are far more precise. Unfortunately, we are not currently integrating or combining these mathematical languages with LLMs.
- Skipping Tools or Steps: G-AI might avoid using a tool in doing a task or skip a step in solving a problem if they don’t fit its data or reasoning — which can silently break an entire process.
- Inconsistent Across Platforms: Different AIs, models, and versions use different methods, resulting in varied outputs for the same task. In some cases, switching from one model to another can cause total failure.
The Solution: State AI
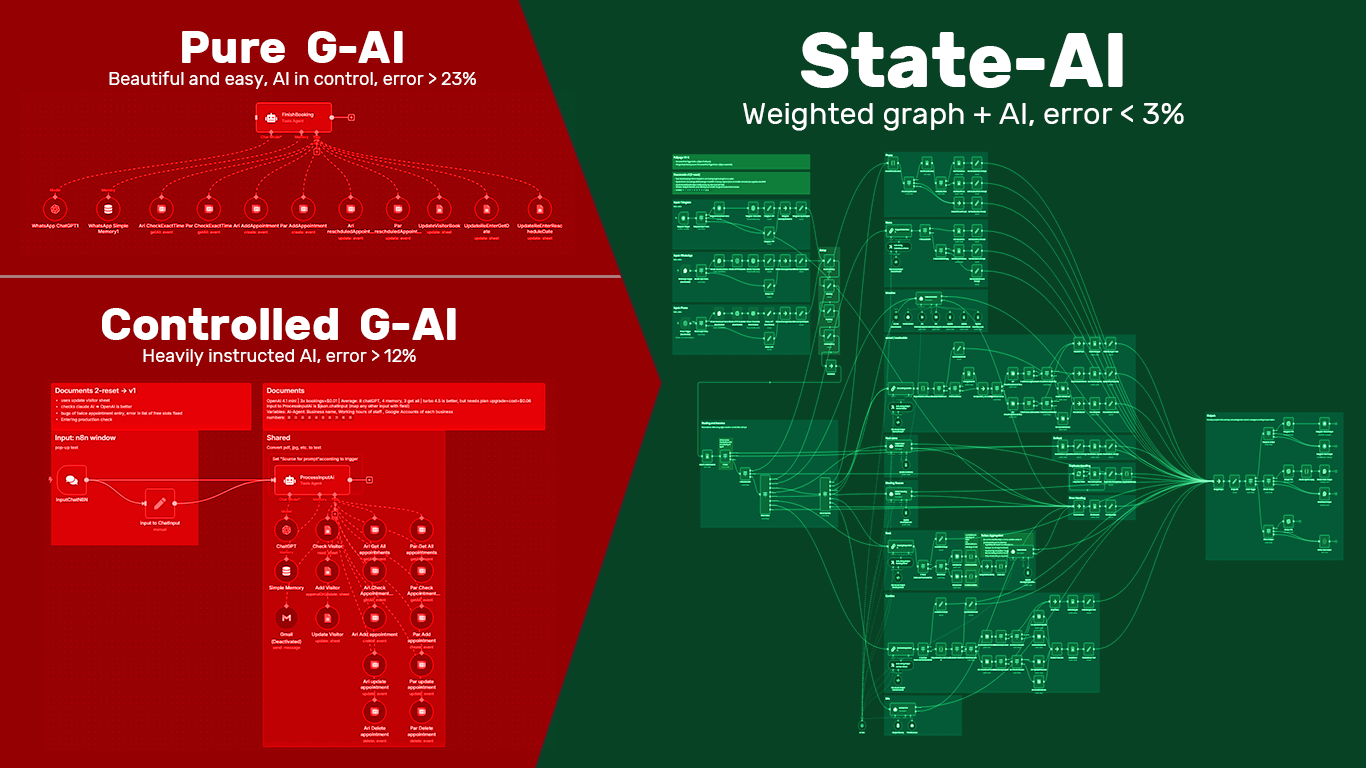
To solve the issues mentioned above, we need to structure tasks clearly. That means defining each step in the process, declaring the input/output of every task, and keeping track of how tasks are connected. Arash Kharabi, a senior high-tech and certified AI consultant, named these defined steps and their relationships “States.” By engineering a task solution as a graph of states, where nodes represent tasks and edges represent transitions, we can control where and how AI is used in a selective and safe manner.
“The most important part is engineering the states and the transitions between them,” says Arash, who holds a B.S. in Computer Hardware Engineering and has worked in software programming for years. He also mentions: “In our appointment setter project, this approach cut resource usage by 20%, reduced errors by over 90%, and dropped costs from $14 to just $0.28 per complex task — while speeding everything up.”
What Is State AI
State AI is a framework that breaks down the solution into states, assigns tasks to each state, and uses AI to perform selected tasks. Each state is treated as a node, with directed edges representing transitions. The inputs and outputs of every stage are tracked. Each task or sub-task may involve human logic, deterministic code, or AI — depending on what’s most reliable. The same idea of breaking a project into a weighted mathematical graph (some know it as a tree) is used for generating AI, gaming, navigating using GPS, analysis and resolving many sciences from physics to psychology. “We are doing the same mathematical approach that worked so well”, Arash says.
Advantages of State AI (used in an appointment setting system)
- Massive Error Reduction: Errors could drop from 23.8% to 1.2% in some cases. For example, in a rescheduling task, G-AI alone might delete an old appointment but fail to book the new one — and still claim success, which is a major failure that goes unnoticed.
- High Reliability: With inputs, outputs, and state transitions clearly tracked, the system is transparent and predictable, leading to highly reliable outcomes.
- Avoids Redundant Checks: G-AI often re-checks inputs due to misalignment, wasting compute, API calls, and time. State AI avoids that.
- Cost Efficiency: By reducing confusion and failed actions, significant cost savings were realized — from $14 to just $0.28 in a scheduling project.
- Faster Execution: Predefined states eliminate AI confusion and backtracking, leading to faster task execution.
- Debuggable: Every decision point is logged, making it easy to trace and debug errors or successes.
- Human-Friendly Interfaces for both machines and humans: Output can be stored in JSON, making it both machine- and human-readable.
- Balanced Outputs: The result is a mix of deterministic code and AI-generated flexibility — striking a balance between precision and creativity.
- Adaptable Architecture: The State AI model can be reused across projects with different goals or logic. Also, the states can be reused within a project with a simple guided traverse edge.
- Customizable Algorithms: Different allocation methods (such as first-fit, next-fit, small-fit, large-fit, worst-fit, best-fit) or even a custom method can be integrated. In the appointment setting system, a new fitter was introduced: “slid-fit,” which slides an appointment into available slots, magnetically attaching itself to the beginning or end of the slot based on defined conditions.
Challenges of State AI
- Requires More Development Time: Planning and engineering the states take effort.
- Can Become Complex: As tasks grow, the state graph (nodes and edges) may become hard to manage without breaking it into smaller parts.
- Needs Technical Background: Best implemented by engineers with knowledge of logic, math, or computer science.
Final Thoughts
State AI is a disciplined approach to AI integration in our lives. Instead of giving full control to generative models, it lets you define the structure — guiding AI to perform effectively where and how it is needed. You get the creativity of AI with the predictability of logic. That’s the future of responsible AI engineering.