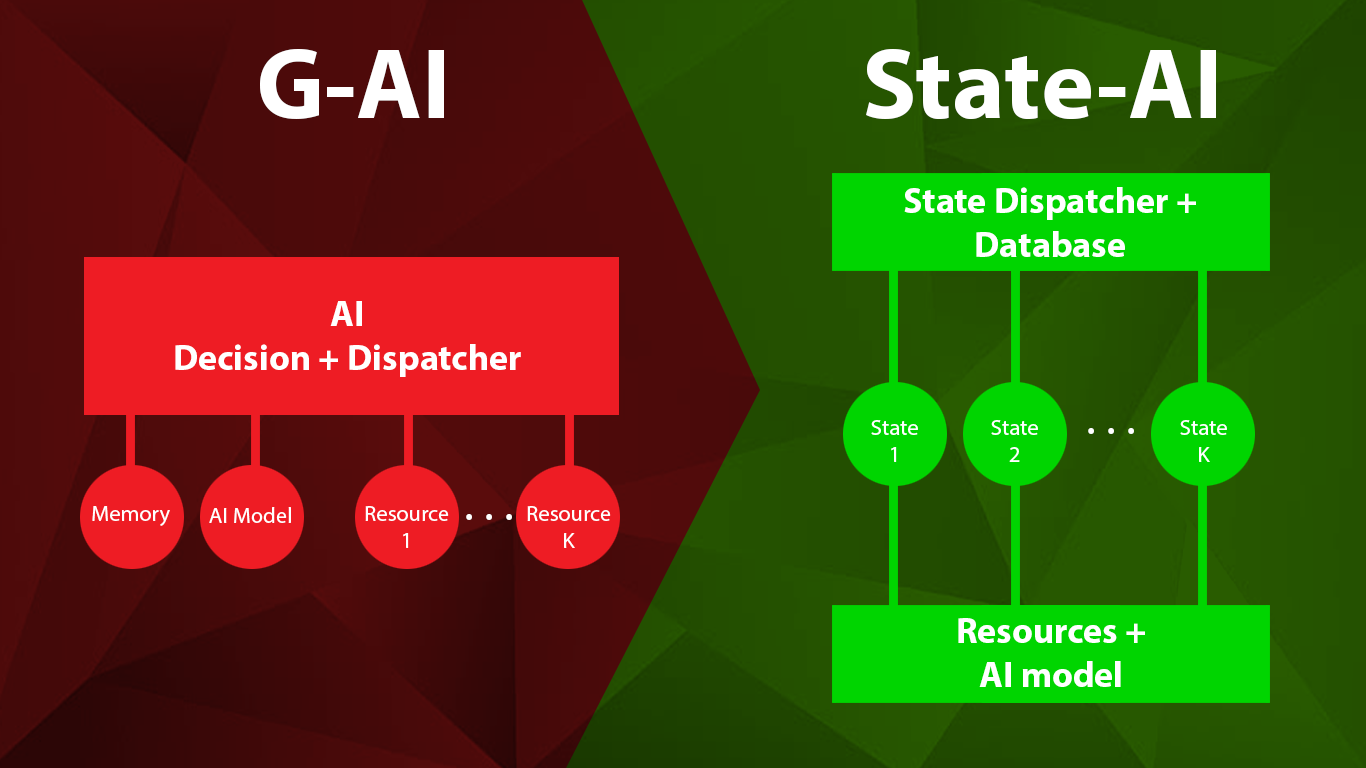
Generative AI (G-AI) is a powerful tool, but it often behaves in ways that make automation unreliable, costly, and difficult to scale. "After three months of experimentation with multiple G-AI engines, our team at DesignAndBusiness developed State AI (S-AI) — a framework designed to mitigate these problems by introducing state-driven workflow control", says Arash Kharabi, who directed the project. With a background in computer engineering and experience running multiple G-AI licenses, he continues: "If you’ve ever finished a project thinking it works, only to watch it fail over and over, you’ll understand why we built this... we all know first-hand how painful these failures can be."
Challenges in Generative AI Automation
Despite its flexibility, Generative AI introduces several structural weaknesses when applied to decision-making and workflow execution:
- Wrong decisions → causing broken workflows and failed automation.
- Inconsistent results → the same input can produce different outputs each run.
- Inefficient resource use → higher costs, delays, and quota overruns.
- Process confusion → tasks are marked “finished” before completion, or repeated unnecessarily.
- Version instability → provider updates change outputs, breaking existing processes.
- Memory issues → mixing up subjects and objects from past inputs.
- Complex definitions → natural language–based logic makes workflows long, confusing, and error-prone.
These issues make G-AI unreliable as the sole driver of automation.
The State AI Approach
State AI (S-AI) addresses these problems by introducing state-based decomposition of workflows:
- State segmentation: Break the overall workflow into discrete, deterministic states.
- Database tracking: Persist state information so execution can resume reliably after failures.
- Multi-agent orchestration: Assign specific AI agents to specific states, with strict role definitions.
- State validation: Enforce constraints and verification rules before moving to the next state.
This approach ensures that workflows remain predictable, reproducible, and resilient to AI inconsistencies.
Benefits of State AI
By enforcing structured states, State AI achieves:
- Reduced error rates: AI outputs are validated within each state before progression.
- Consistent results: Same inputs → same outputs across runs.
- Cost efficiency: Controlled state execution minimizes unnecessary API calls.
- Process integrity: Prevents skipped or repeated steps.
- Faster performance: Avoids unnecessary usages, loops and checks.
- High accuracy and quality: Each agent focuses on a narrow, well-defined task.
Implementation Requirements
To implement State AI effectively, you’ll need:
- Development time — to define the states and workflow structure.
- Database integration — for state persistence, validation, and rollback.
- System design knowledge — to architect multi-agent coordination and error handling.
The upfront complexity is higher than standard G-AI pipelines, but the long-term gains in reliability, cost savings, and performance outweigh the investment.
Who Should Use State AI?
Anyone building or managing projects that rely on G-AI for decision-making will benefit from State-AI. Whether you’re an engineer, designer, business owner, or researcher, State-AI provides the structure that keeps AI workflows from going off the rails.
- AI engineers building decision-making systems.
- Automation developers managing multi-step workflows.
- Businesses relying on G-AI for critical operations.
The most important NOTE
Modern artificial intelligence and computer systems are fundamentally built on discrete mathematics, a branch of math that deals with distinct, separate elements rather than continuous quantities. Unlike traditional or “old-age” mathematics, which focuses on equations, calculus, and smooth curves to describe natural phenomena, discrete math models information using nodes and edges — the language of graphs, networks, and logical structures. This shift allows machines to represent relationships, decisions, and data connections in a digital world made up of binary states (0s and 1s). In essence, while classical math explains how things change, discrete math explains how things connect, forming the backbone of algorithms, data structures, and the intelligent systems that drive AI today..
Conclusion
State AI (S-AI) transforms G-AI from a non-deterministic black box into a structured, state-driven workflow engine. By decomposing processes into verifiable states and orchestrating multiple agents under strict rules, State-AI dramatically reduces errors, increases consistency, and ensures production-ready reliability.